
This article will explore the fundamental concept of market structure and its significance in economic analysis. We’ll delve into the different types of market structures, examining their characteristics and implications. We’ll also be discussing the key participants involved in market structure. Furthermore, we will provide insights into tips for effectively utilising market structure analysis in decision-making processes, enabling readers to navigate the complexities of economic environments with greater understanding and proficiency.
Market structure refers to a market's organisational framework and characteristics, determining how goods and services are exchanged and prices are established. Market structure in Forex encompasses various elements such as the types of participants, regulations, and the level of competition.
Market structure holds immense significance in trading. By analysing market structure, traders can:
The participants of Forex market structure are the following:
The Central Bank and Government
The South African Reserve Bank (SARB) acts as the central bank and plays a pivotal role in the country's market structure. It formulates and implements monetary policies, regulates the banking sector, and manages foreign exchange reserves. Additionally, the government influences market structure through fiscal policies, legislation, and economic reforms aimed at promoting financial stability and sustainable economic growth.
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are key participants in financial market structure, providing a wide range of banking services such as deposit-taking, lending, and foreign exchange transactions. Some prominent commercial banks in South Africa include Standard Bank, ABSA Group, FirstRand Limited, and Nedbank Group. These banks contribute to market liquidity, facilitate capital formation, and play a crucial role in intermediating funds between savers and borrowers.
Transnational Corporations
Transnational corporations operating in South Africa, including multinational companies and foreign investors, significantly influence the country's market structure. These corporations operate across various sectors, such as mining, manufacturing, telecommunications, and finance, contributing to economic development, job creation, and foreign direct investment. Examples include Anglo American, Sasol, MTN Group, and Naspers.
Retail Traders
Retail traders constitute a diverse group of individual investors who participate in financial markets through online trading platforms, brokerages, and investment funds. They play an increasingly significant role in market structure, contributing to market liquidity, trading volumes, and price discovery.
Institutional Traders
Institutional traders encompass entities such as pension funds, insurance companies, hedge funds, and asset management firms that manage large investment portfolios on behalf of institutional clients or shareholders. Institutional traders wield substantial influence over market structure due to their significant capital allocation and trading activities.
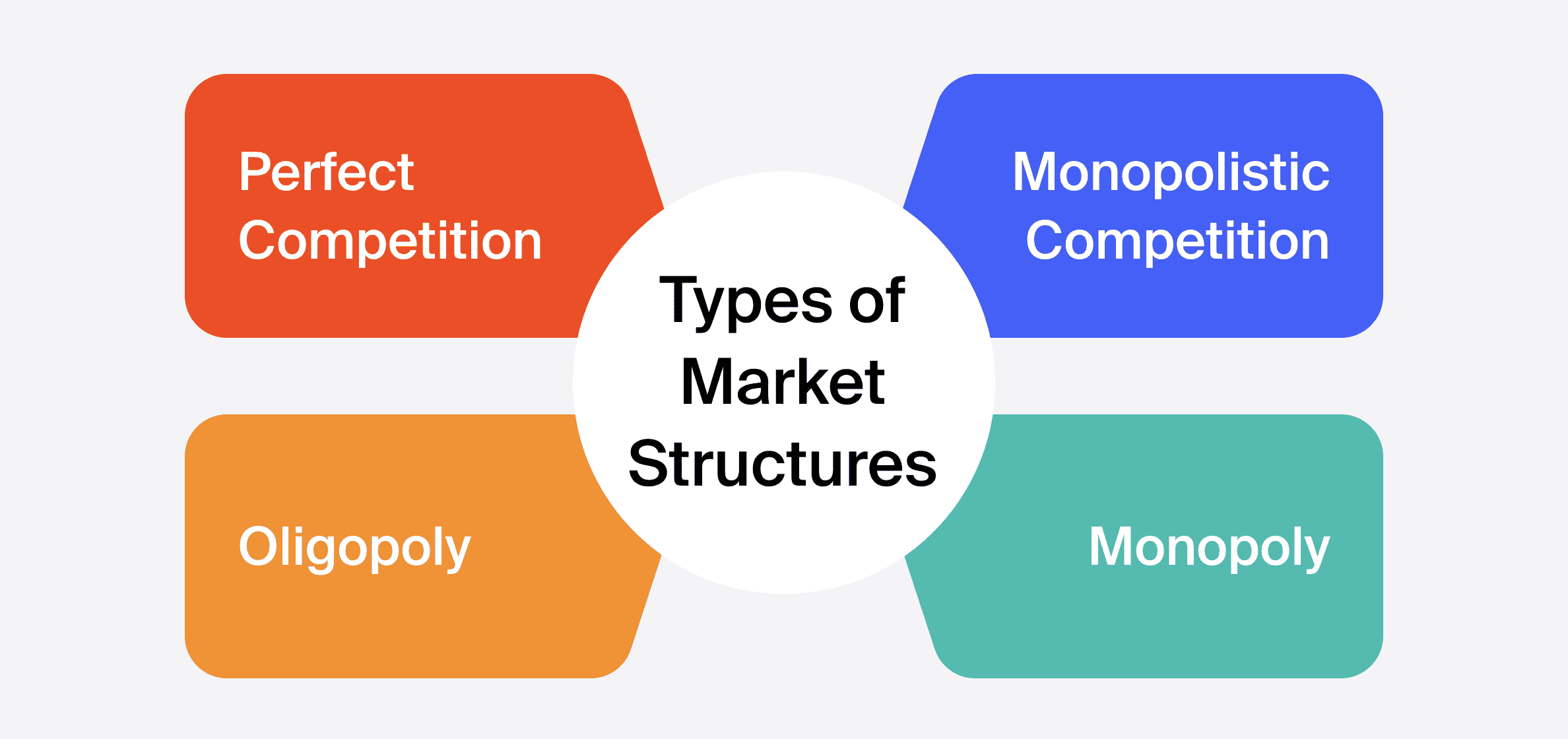
There are various types of market structures, each characterised by unique features and degrees of competition:
Perfect Competition
Perfect competition represents a theoretical market structure where numerous small firms compete with homogeneous products, and entry and exit barriers are low. In South Africa, perfect competition may be observed in specific segments of the agricultural sector, where many small-scale farmers produce identical goods such as grains or vegetables.
Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition characterises markets with many firms producing differentiated products, allowing firms to exert some degree of market power through branding and product differentiation. Sectors such as retail, restaurants, and consumer goods often exhibit monopolistic competition, with firms competing based on product differentiation and marketing strategies.
Oligopoly
An oligopoly occurs when a few large firms dominate a market, leading to intense competition and potential collusion among competitors. Industries such as telecommunications, banking, and mining are examples of oligopolistic markets, where a few major players wield significant market power and influence pricing and market dynamics.
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a single firm controls the entire market, with no close substitutes available. While pure monopolies are rare, South Africa has seen monopoly power in sectors such as electricity distribution, where state-owned enterprises or private companies hold exclusive rights to provide essential services in specific regions.
Several factors influence the market structure Forex, shaping the competitive landscape and dynamics within various industries:
The South African Reserve Bank plays a pivotal role in shaping market structure through various monetary policy tools and regulatory measures:
Here are some tips for using market structure to your advantage:
Utilise Several Time Frames
Analysing market structure across multiple time frames provides a comprehensive view of price movements and trends. Traders should consider using daily, hourly, and shorter-term charts to identify key support and resistance levels, trend directions, and potential entry and exit points.
Analyse Various Assets
Diversifying across different asset classes allows traders to capitalise on diverse market opportunities and mitigate risks. By analysing market structure across various assets, traders can identify correlations, market inefficiencies, and trading signals.
Utilise Technical Indicators
Technical indicators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Fibonacci retracements, complement market structure analysis by providing additional insights into price momentum, overbought or oversold conditions, and trend reversals. Traders should integrate technical indicators into their analysis to validate market structure signals and enhance trading decisions.
Keep Watch for Role Reversals
Identifying role reversals, where previous support levels become resistance and vice versa, is crucial for understanding market structure shifts. Traders should monitor price action around key levels and observe how market participants react to identify potential role reversals and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Be Mindful of Context
Considering broader economic, geopolitical, and market factors provides context for interpreting market structure signals. Traders should stay informed about relevant news, events, and developments that may impact market sentiment, volatility, and trends, allowing them to make informed decisions within the context of market structure analysis.
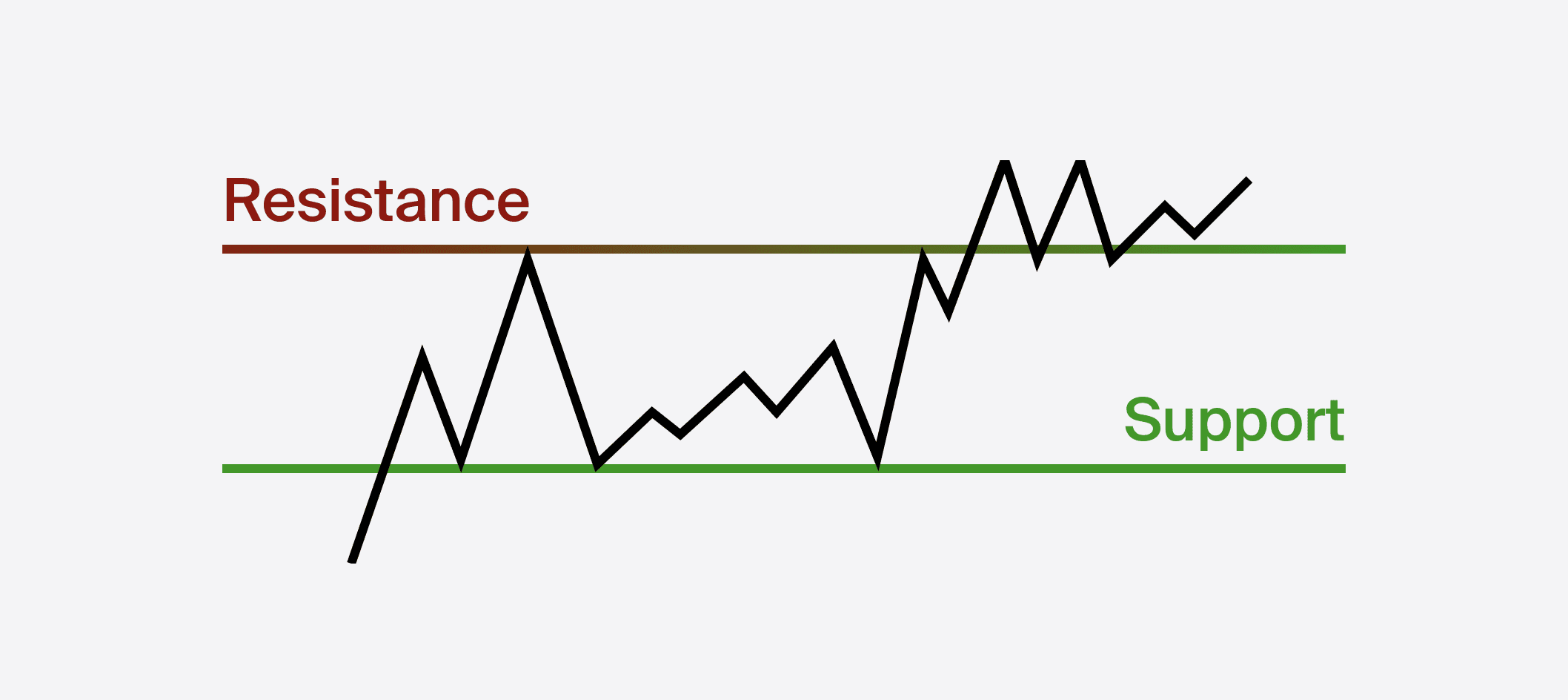
Support and resistance levels play important roles in determining market structure and guiding trading decisions:
Effectively recognising and interpreting support and resistance levels enables traders to make informed trading decisions, manage risk, and identify potential entry and exit points within the market structure.
Bottom Line and Key Takeaways
Understanding market structure is essential for traders. By analysing market participants, types of market structure, and factors influencing it, traders can develop effective trading strategies, manage risks, and capitalise on opportunities presented by market dynamics.
The SARB's monetary policy decisions, exchange-rate interventions, reserve management practices, and regulatory oversight play a crucial role in shaping market structure and maintaining the stability and efficiency of financial markets.
Maboko holds a BTech in Metallurgical Engineering and has been in the financial market for over 6 years. He has experience in market analysis and systematic trading strategies.
Regulatory changes can influence market structure by altering the competitive landscape, liquidity conditions, and investor sentiment, impacting asset prices and trading strategies.
Technological advancements such as algorithmic trading, high-frequency trading, and electronic communication networks have transformed market structure by enhancing market efficiency, reducing transaction costs, and increasing trading volumes.
Traders can analyse market structure using technical analysis tools such as trend lines, support and resistance levels, moving averages, and chart patterns to identify trading opportunities and manage risk effectively.
© 2025 BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD.
BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD is an authorised Financial Service Provider and is regulated by the South African Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSP No.51404). BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD Proprietary Limited trading as BROKSTOCK. BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD t/a BROKSTOCK acts solely as an intermediary in terms of the FAIS Act, rendering only an intermediary service (i.e., no market making is conducted by BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD t/a BROKSTOCK) in relation to derivative products (CFDs) offered by the liquidity providers. Therefore, BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD t/a BROKSTOCK does not act as the principal or the counterparty to any of its transactions.
The materials on this website (the “Site”) are intended for informational purposes only. Use of and access to the Site and the information, materials, services, and other content available on or through the Site (“Content”) are subject to the laws of South Africa.
Risk notice Margin trading in financial instruments carries a high level of risk, and may not be suitable for all users. It is essential to understand that investing in financial instruments requires extensive knowledge and significant experience in the investment field, as well as an understanding of the nature and complexity of financial instruments, and the ability to determine the volume of investment and assess the associated risks. BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD pays attention to the fact that quotes, charts and conversion rates, prices, analytic indicators and other data presented on this website may not correspond to quotes on trading platforms and are not necessarily real-time nor accurate. The delay of the data in relation to real-time is equal to 15 minutes but is not limited. This indicates that prices may differ from actual prices in the relevant market, and are not suitable for trading purposes. Before deciding to trade the products offered by BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD, a user should carefully consider his objectives, financial position, needs and level of experience. The Content is for informational purposes only and it should not construe any such information or other material as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice. BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD will not accept any liability for loss or damage as a result of reliance on the information contained within this Site including data, quotes, conversion rates, etc.
Third party content BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD may provide materials produced by third parties or links to other websites. Such materials and websites are provided by third parties and are not under BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD's direct control. In exchange for using the Site, the user agrees not to hold BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD, its affiliates or any third party service provider liable for any possible claim for damages arising from any decision user makes based on information or other Content made available to the user through the Site.
Limitation of liability The user’s exclusive remedy for dissatisfaction with the Site and Content is to discontinue using the Site and Content. BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD is not liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, consequential, special or punitive damages. Working with BROKSTOCK SA (PTY) LTD you are trading share CFDs. When trading CFDs on shares you do not own the underlying asset. Share CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. A high percentage of retail traders accounts lose money when trading CFDs with their provider. All rights reserved. Any use of Site materials without permission is prohibited.